Test
cpbooster provides the following command for you to easily test your program against
all available test cases.
cpb test <filePath>
or the alias for test which is just t.
cpb t <filePath>
This command will automatically compile your program everytime you run it. See Test Without Recompiling for details on how to avoid recompiling your program each time.
Executable File Details
The executable file will be located in your current directory and its name will
match with the name of the source file except for the extension, which will be .exe.
For example, if your source file name is ProblemA.cpp then the executable file
name will be ProblemA.exe.This is because cpbooster uses filenames to associate
everything (See File Structure for better understanding).
If you wish to save the executable file with a different name,
you can specify it in your languages.<lang>.command.
Test With A Single Test Case
You can specify the test case, using the --testId flag or its alias -t.
cpb t <filePath> -t <number>
<number> should match with the numeric suffix of the corresponding .in and .ans files
See File Structure for better understanding.
Test Without Recompiling
You can tell cpbooster to run the tests using the last compiled version of your program
by passing the flag --noCompile or its alias --nc.
cpb t <filePath> --nc
By using this flag, cpbooster will assume that there is a corresponding executable file
for your program. Remember that the name of the executable file must be the same as the
source file, except for the extension which must be .exe. Unless you specified otherwise
in languages.<lang>.command.
Supported Veredicts
- AC (Accepted Solution)
- WA (Wrong Answer)
- CE (Compilation Error)
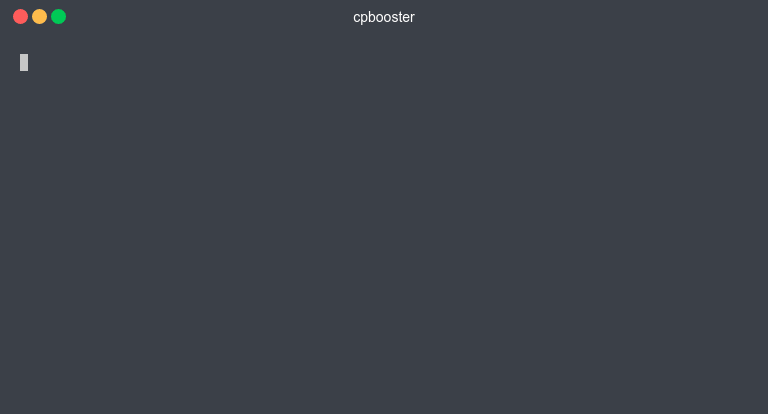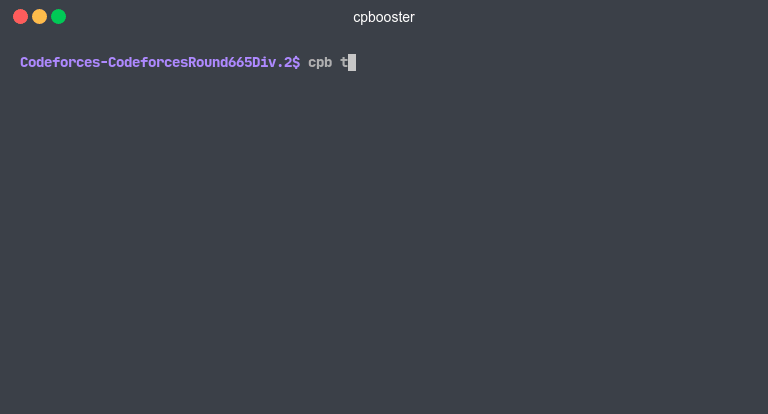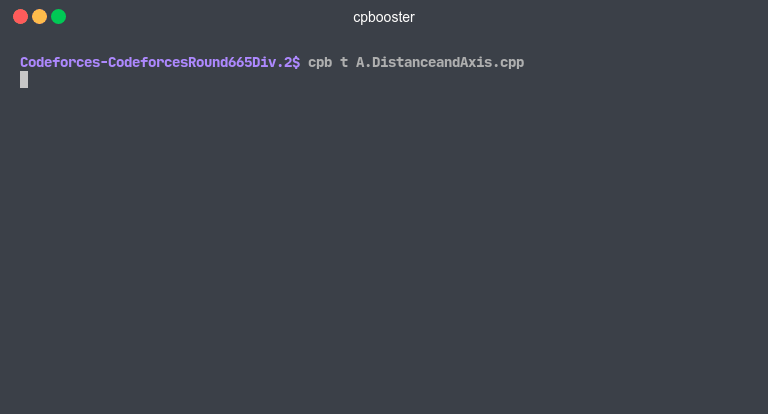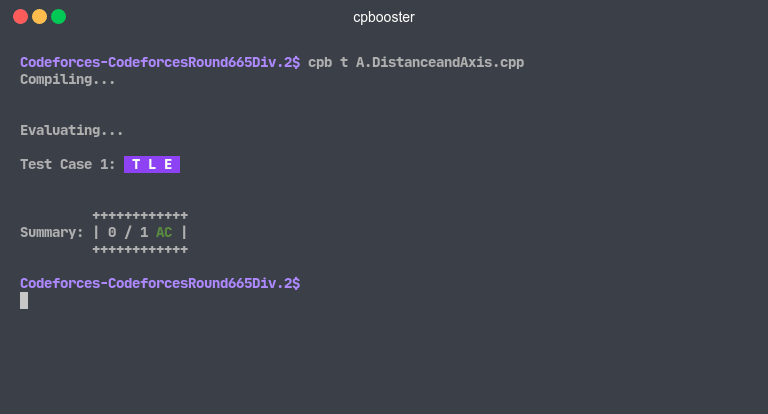
- TLE (Time Limit Exceeded)
- RTE (Runtime Error)
How does it work?
This sections explains How each possible output of the test command work.
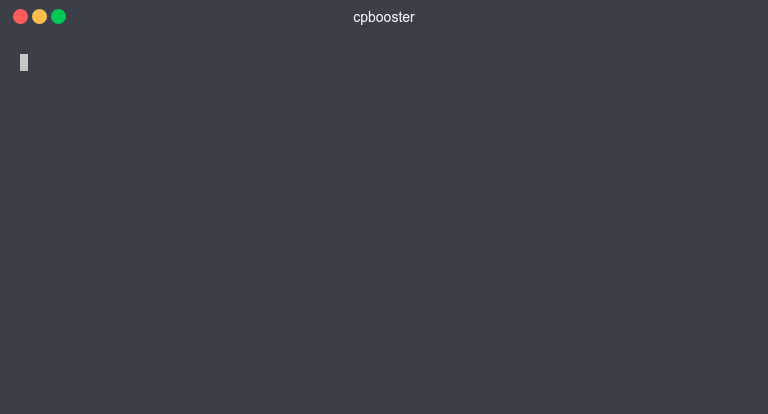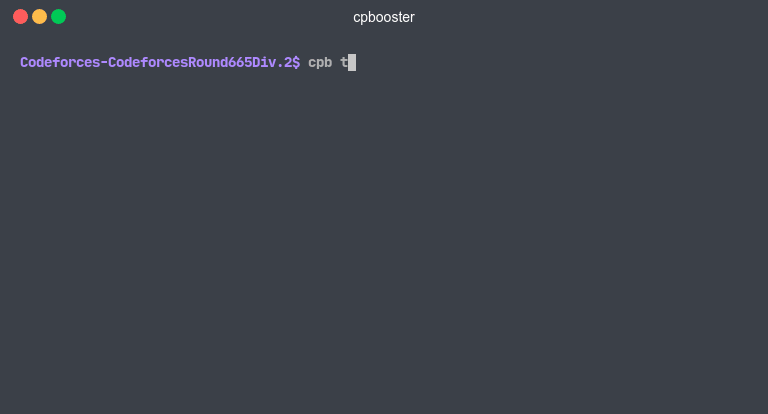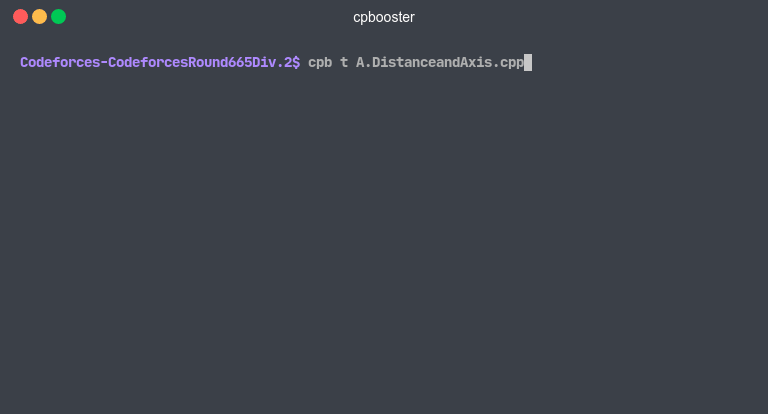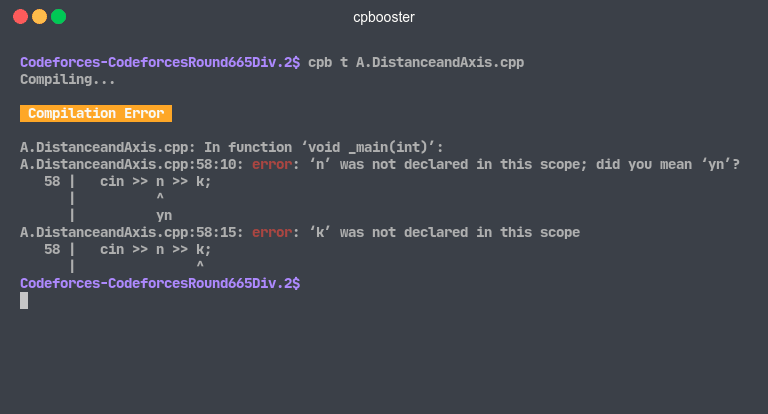
Compilation Error
If your code needs compilation (cpp, java, ...), this will be the first thing that cpbooster will
try to do, unless the --noCompile flag was used.
Demo
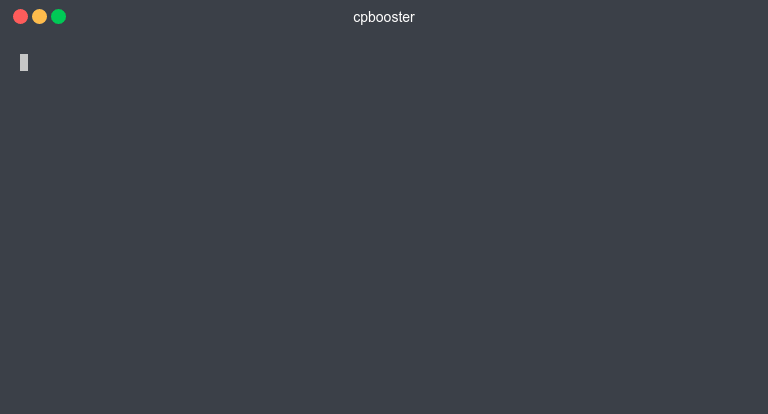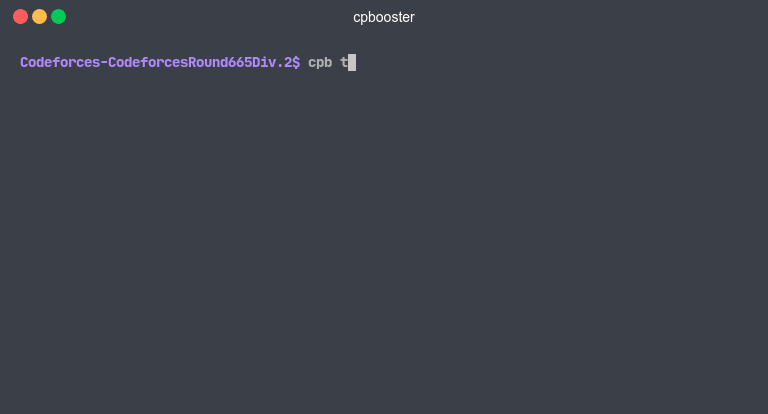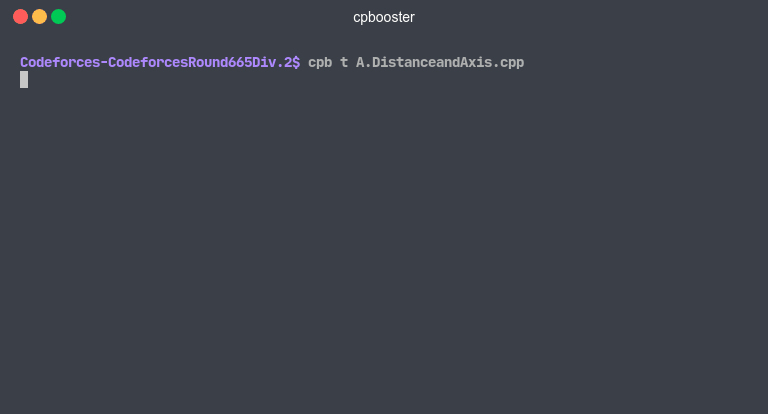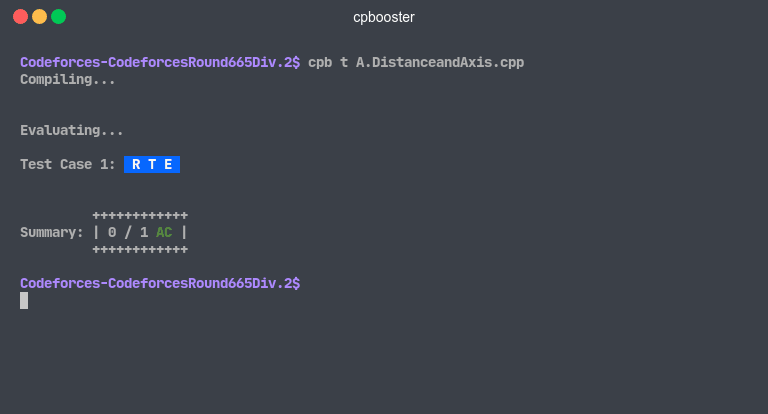
Runtime Error
cpbooster detects that there was a runtime error if your program exited with a status code different from 0
or if there were no corresponding .in and .ans files (See File Structure for better understanding).
Demo
Time Limit Exceeded
To detect that the execution of a certain program has exceeded the time limit, cpbooster requires to know
which is this time limit beforehand, the default value is 3000 milliseconds which equivalent to 3 seconds.
To use a different value, the string time-limit: followed by the time limit in numeric format as milliseconds
should be written somewhere in the source file as a commented line.
Examples:
C++ | Python |
|---|---|
| |
This line will be automatically added at the top of your source file with the default value
when running cpb clone or cpb create.
Demo
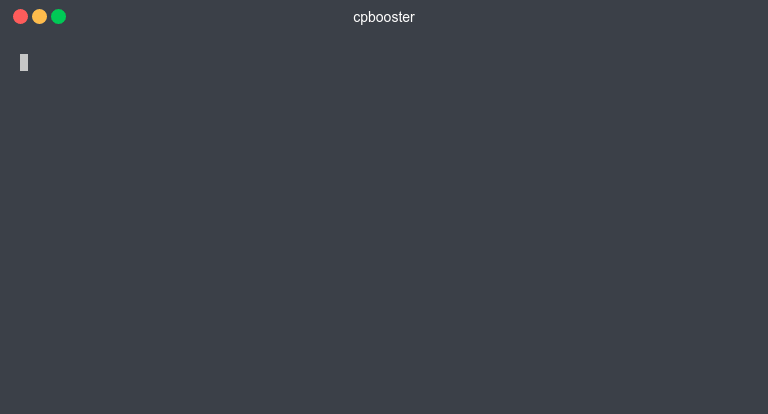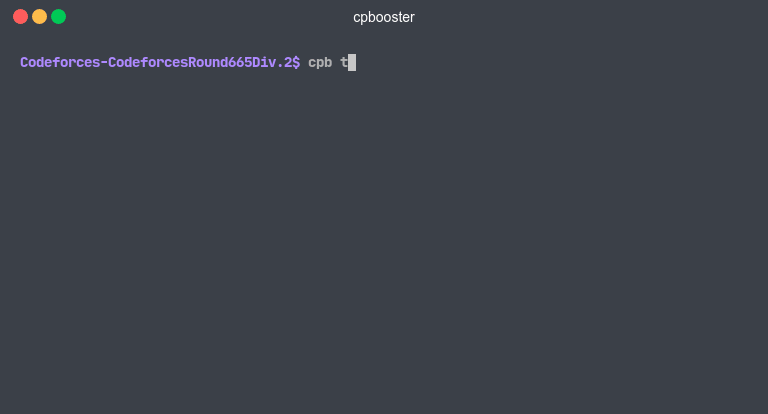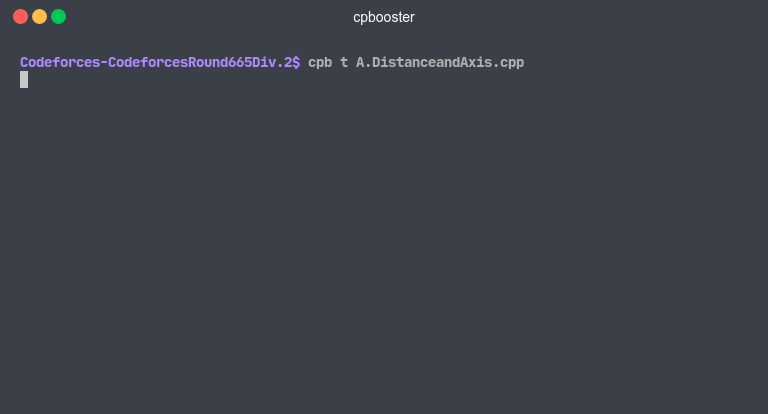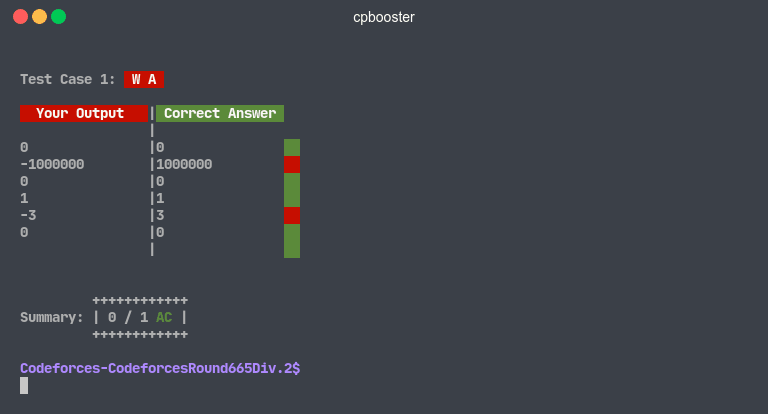
Wrong Answer
Each time you run a test, cpbooster will create one or more .outX files (in the same directory as the
source file) which will correspond to your program's output when using the correponding .inX file as
input.
Each .outX file will be compared against the corresponding .ansX file and if
there are differences, they will be printed beautifully.
-
Each
.in,.ansand.outfile will and must have the same name as the source file associated with them. This is becausecpboosteruses file names to make associations. See File Structure. -
Xshould be an integer number and every.in,.ansand.outfile associated with a certain test case, must have the same numeric suffixX.
Demo
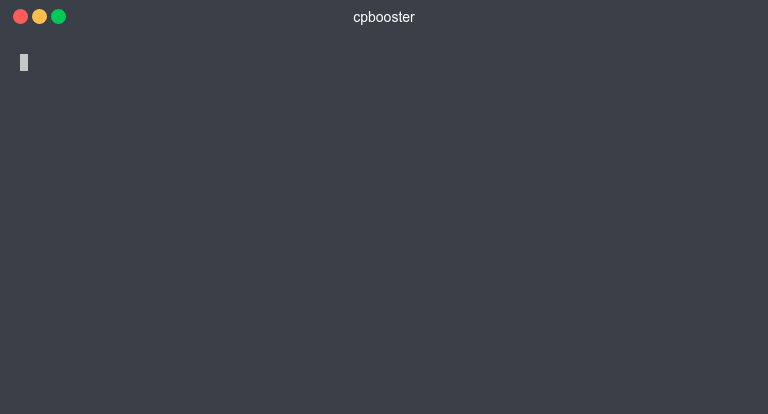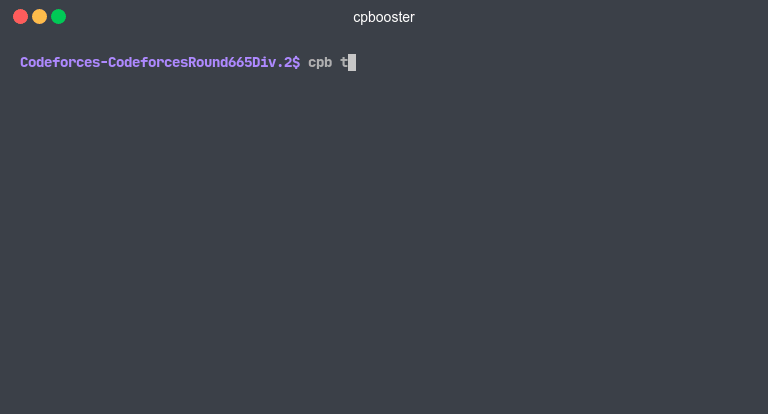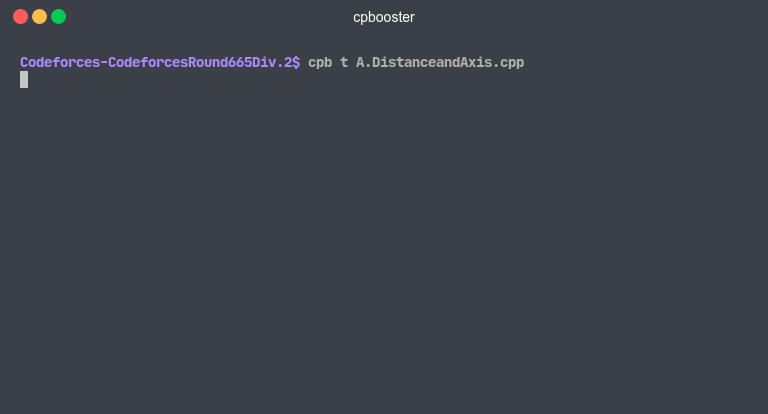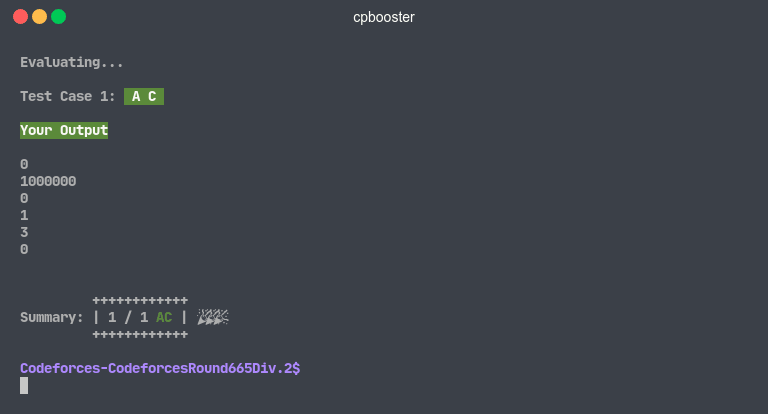
Accepted Solution
If there were no errors or differences between the .out and .ans files, cpbooster will tell you that you have an
Accepted Solution.
cpbooster will also tell you if your solution has extra leading or trailing blank spaces.
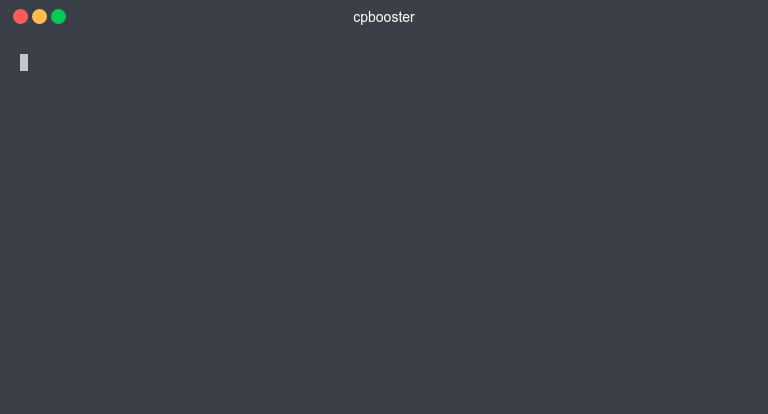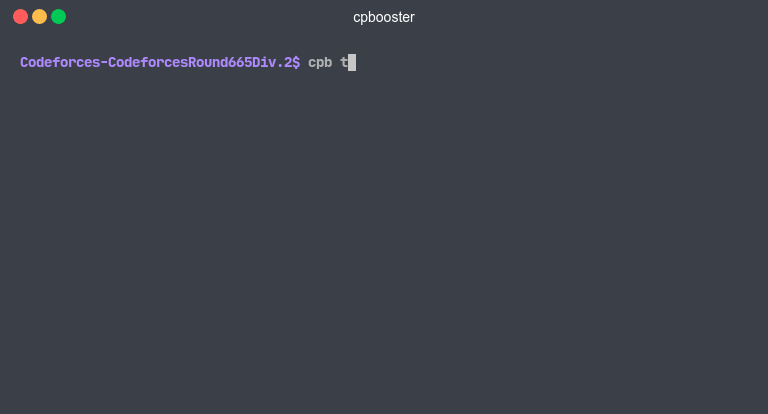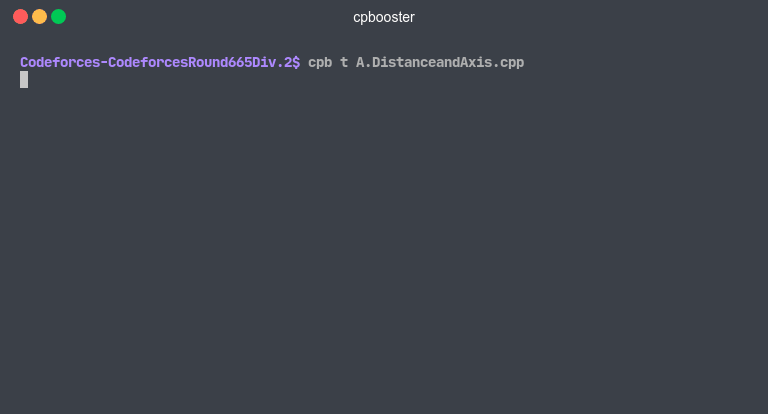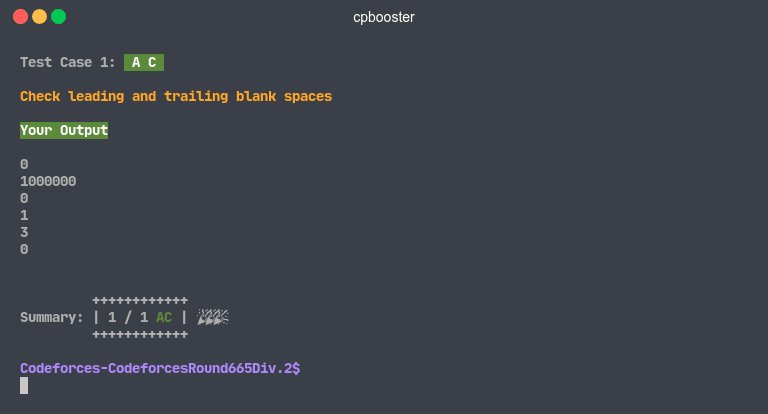
Demo